何に使うかは決めていないけれどM5Stack Core2 IoT開発キットを買ってみた。
スイッチをいれるとすでにアプリが入っていた。
 なんかすごい。
なんかすごい。
Hello World
新しいマイコンを手に入れたらまずはLEDチカチカかHello World。
VSCode + PlatformIOで開発環境を用意1してM5Stack Core2のディスプレイにHello Worldを表示してみるとする。
| |
 あっすごい。簡単。
あっすごい。簡単。
赤外線リモコン信号を送受信してみる
 M5Stack用赤外線送受信ユニットを一緒に買っておいたので赤外線リモコン信号を解析して見ようかと思う。
M5Stack用赤外線送受信ユニットを一緒に買っておいたので赤外線リモコン信号を解析して見ようかと思う。
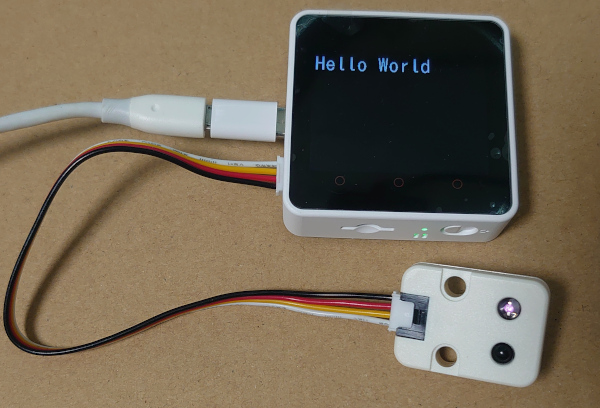 M5Stack Core2とM5Stack用赤外線送受信ユニットをつないでみた。
M5Stack Core2とM5Stack用赤外線送受信ユニットをつないでみた。
PORT番号は回路図によると
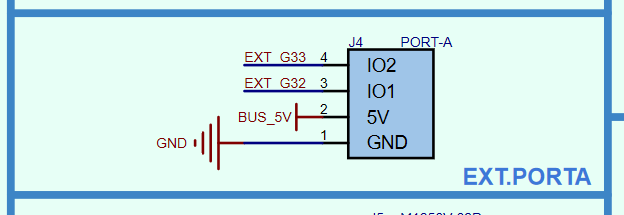 G33/G32だと。
G33/G32だと。
赤外線送受信ユニットの方は
 なので
なので
| ピン番号 | M5Stack Core2 | M5Stack用赤外線送受信ユニット |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | GND |
| 2 | 5V | 5V |
| 3 | GPIO32 | OUT(赤外線送信) |
| 4 | GPIO33 | IN(赤外線受信) |
こうだね。
IRremoteESP8266による受信
IRremoteESP8266 という素敵なライブラリがあるので有難く使わしてもらいます。
| |
赤外線リモコン信号受信サンプルソース(IRrecvDumpV3)を
M5 Core2で動くようにカスタマイズして
| |
Panasonic製エアコンリモコンで送信した「暖房23℃」の信号を読ませてみると。
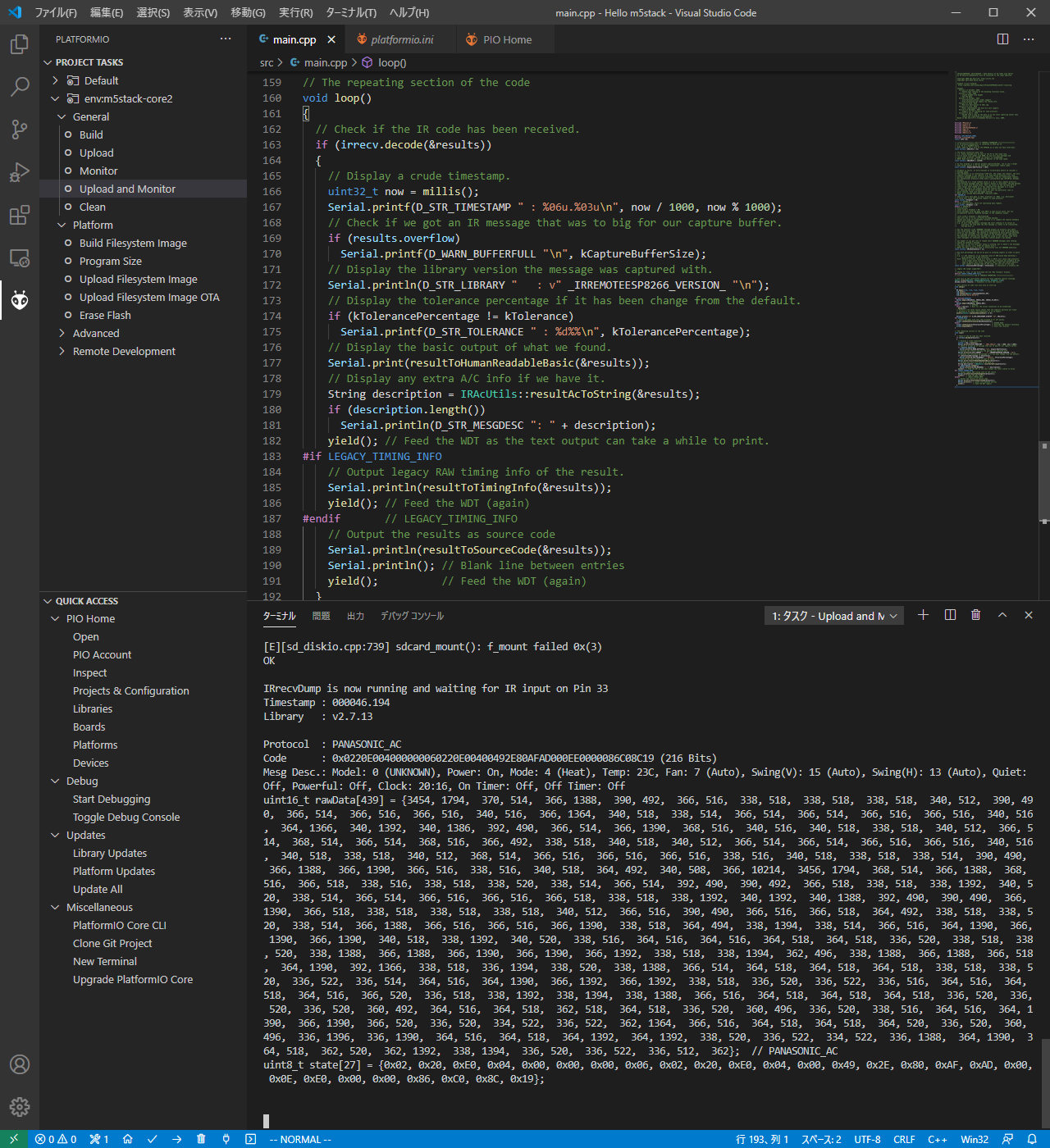
これはシリアルコンソールに出力された内容
| |
- Protocol: PANASONIC_AC
- Model: 0 (UNKNOWN)
- Power: On
- Mode: 4 (Heat)
- Temp: 23C
- Fan: 7 (Auto)
- Swing(V): 15 (Auto)
- Swing(H): 13 (Auto)
- Quiet: Off
- Powerful: Off
- Clock: 20:16
- On Timer: Off
- Off Timer: Off
ちゃんとあってる。すごいねー。
IRremoteESP8266による送信
受信が問題なくできたので続いて送信をしてみる。
赤外線リモコン信号送信サンプルソース(CommonAcControl)を
カスタマイズして
| |
ビルドして書き込むとこう表示されるから

画面のどこでも押すと

赤外線信号が送信されて(すでに動いている)エアコンのファンが最大風量になった。
赤外線リモコンがこんなに簡単にできた。すごいね。
ほんとマイコンのプログラミングも便利になったね。
今時はんだ付けとか必要ないねんな。
7セグメントディスプレイを使ってみる
製品を買ってつないだだけで終わるのもなんか味気ないので, LEDチカチカの代わりに7セグメントディスプレイに数字を表示してみる。
今回は M5Stack Core2のI2CバスにPCF8574を使って7セグメントディスプレイをつなぐ。
使った7セグメントディスプレイのデーターシートはこれです。
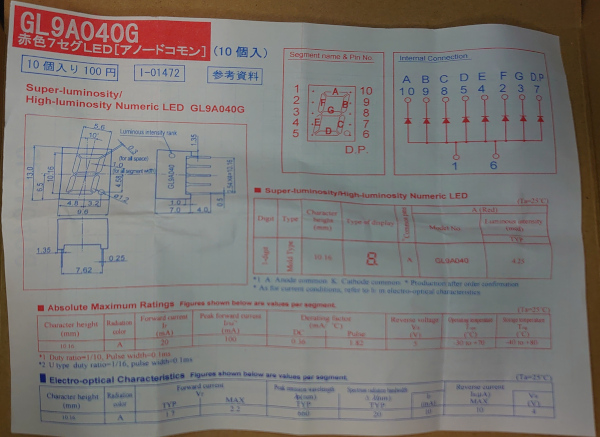
PCF8574のデーターシートからピン配列とI2Cアドレス
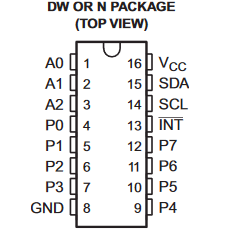
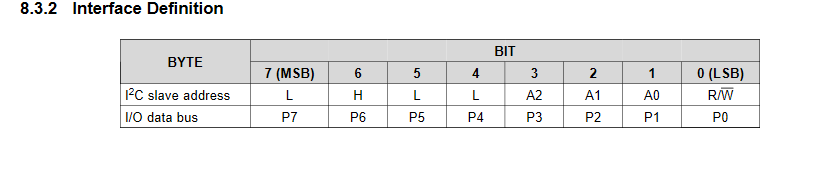
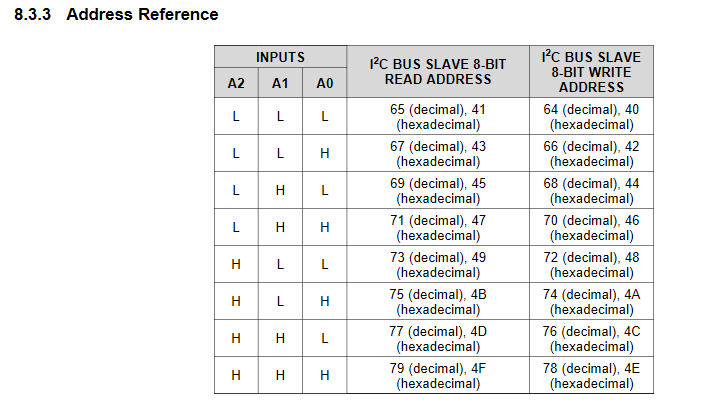
今回は(アドレス選択)A0,A1,A2共にGNDに接続したので
0100000x = 0x20(I2Cアドレス)
01000000 = 0x40(write address)
01000001 = 0x41(read address)
になる(ソースコードで指定するのはI2Cアドレス)。
| |
ビルドして実行すると。
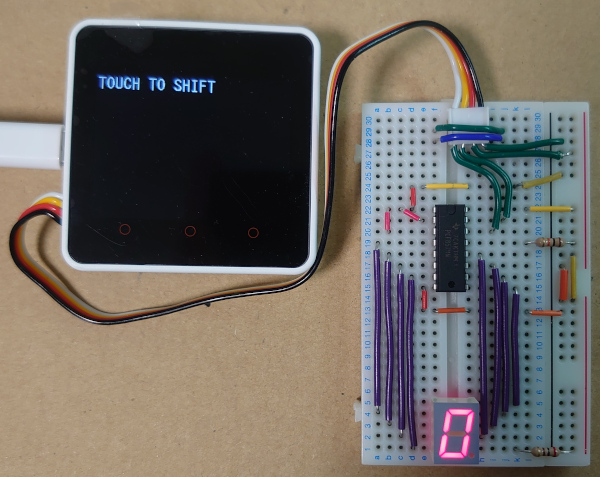
画面を押すと
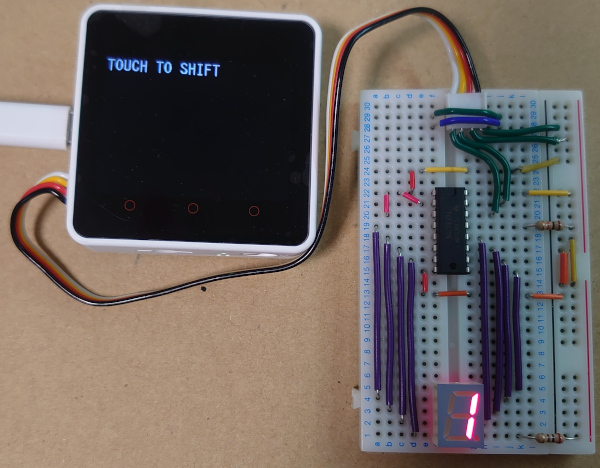
画面を押すたびに0~9までを繰り返す。
回路図を書くのが面倒なので, 接続は写真をよく見てください。
面倒だから7セグディスプレイの共通線側に電流制限抵抗を付けているけどこれはマネしないでね。
正しくは共通線側を電源直結にして7セグディスプレイのピンそれぞれに抵抗を付けるように接続してください。
ほんとマイコンのプログラミングも便利になったね。(2回目)
